React笔记
React笔记
安装脚手架命令
npx
npx create-react-app my-app
(npx comes with npm 5.2+ and higher, see instructions for older npm versions)
npm
npm init react-app my-app
npm init <initializer> is available in npm 6+
Yarn
yarn create react-app my-app
yarn create is available in Yarn 0.25+

原生开发
JS改变某个标签的文字
// 原生开发 -- 命令式编程
let message = "Hello World"
const titleEL = document.getElementsByClassName("title")[0]
titleEL.innerHTML = message
const btnEL = document.getElementsByClassName("btn")[0]
btnEL.addEventListener("click", e => {
console.log("按钮发送了点击")
message = 'Hello React'
titleEL.innerHTML = message
})
// React -- 声明式编程
React开发
React开发需要以来的库
- react:核心文件
- react-dom:React渲染不同平台
- babel:jsx转换为React代码
<!-- 加载 React。-->
<!-- 注意: 部署时,将 "development.js" 替换为 "production.min.js"。-->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17/umd/react.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17/umd/react-dom.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/babel-standalone@6/babel.min.js"></script>
重构原生代码
重构上述更改文字的代码,使用React
let message = "Hello World";
function btnClick() {
message = 'Hello React'
// 与vue 不同,在React变量改变不会渲染,要手动渲染
render()
}
function render() {
// <h2></h2> JSX代码
// JSX特点:多个标签最外层(根)只能有一个标签
ReactDOM.render(
<div>
<h2>{message}</h2>
<button onClick={btnClick}>改变文本</button>
</div>,
document.getElementById('app')
)
}
render()
再次重构React代码,使其标准化:
//封装APP
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
// this.message = 'Hello World'
this.state = {
message: 'Hello World'
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>{this.state.message}</h2>
<button onClick={this.btnClick.bind(this)}>改变文本</button>
</div>
)
}
btnClick() {
console.log(this);
// this.state.message = 'Hello React'
// 不能手动调用this.render()
// 也不能使用this.state.message
// 要使用setState传递对象
this.setState({
message: 'Hello React'
})
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, document.getElementById('app'))
注意点
- 集成时,React.Component中的‘C’应该大写
- construct中的state带this
- render中需要渲染的变量除了带上单胡须'{}'外,还要带上this.state.变量
- 注意ReactDOM.render中的render不要拼写错误
JSX语法 & 语法补充
类的语法补充
ES5创建一个类
// ES5中定义类
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
// 类中定义函数
Person.prototype.running = function() {
console.log(this.name, this.age, "running");
}
var p = new Person("why", 18)
console.log(p.name, p.age)
p.running()
ES6创建一个类
// ES6中通过class创建类
class Person {
// 构造方法, 方法名固定
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
// 定义方法
running() {
console.log(this);
console.log(this.name, this.age, 'running');
}
}
const p = new Person('why', 18)
console.log(p.name, p.age);
p.running()
ES6中继承父类:
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
running() {
console.log('running');
}
}
class Student extends Person{
constructor(name, age, sno) {
// 子类必须初始化父类
super(name, age)
this.sno = sno
}
}
const stu = new Student('Student:why', 18, 100)
console.log(stu.name, stu.age, stu.sno)
stu.running()
案例练习 -- 实践for循环
- 方法一是利用for (element of array)
- 方法二是用ES6语法中的map实现。注:外边是一个大括号
class App extends React.Component{
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
message: 'Hello World',
movies: ['大话西游', '盗梦空间', '星际穿越', '流浪地球']
}
}
render() {
const liArray = []
for (let movie of this.state.movies) {
liArray.push(<li>{movie}</li>)
}
return(
<div>
<h2>电影列表1</h2>
<ul>
{liArray}
</ul>
<h2>电影列表2</h2>
<ul>
{
this.state.movies.map(one => {
return <li>{one}</li>
})
}
</ul>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, document.getElementById('app'));
案例联系 -- this的运用
- 根据目前所学的方法,如果方法中要使用this,必须bind(this),不然就是undefined
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
counter: 0
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>当前计数:{this.state.counter}</h2>
{/* 绑定this,方便方法使用this */}
<button onClick={this.increment.bind(this)}>+</button>
<button onClick={this.decrement.bind(this)}>-</button>
</div>
)
}
increment() {
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter + 1
})
}
decrement() {
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter - 1
})
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
JSX语法
React 使用 JSX 来替代常规的 JavaScript。
JSX 是一个看起来很像 XML 的 JavaScript 语法扩展。
与Vue不同,Vue使用的是模板语法(v-if、v-for)
书写规范
只能有一个根元素
为了方便阅读,在render函数中的return后加入'()'
JSX可以是单标签,也可以双标签
- 单标签尾巴必须是'/>' ,如下所示
注释书写
render() {
return (
<div>
{/* 我是一个注释 */}
Hello World
</div>
)
}
嵌入变量/数据
纲要:
- {}中可以显示的内容
- {}中不可以显示的内容。为什么?如果非要显示如何使用?
- JSX对象能用{}显示吗?
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
// 在{}中可以正常显示的内容
name: 'rzy',
age: 18,
names: ['abc', 'cba', 'nba'],
// 在{}不能显示的内容/忽略
// 为什么?真实渲染时经常会作判断,例如:三元运算符,判断为null就不会显示,不然容易出BUG
// 如果需要渲染出来
test1: null,
test2: undefined,
test3: false,
// 对象不能作为jsx的子类
friend: {
name: 'why',
age: 40
}
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>{this.state.name}</h2>
<h2>{this.state.age}</h2>
<h2>{this.state.names}</h2>
<h2>{this.state.test1}</h2>
<h2>{this.state.test2}</h2>
<h2>{this.state.test3}</h2>
{/* 硬显示 */}
<h2>{this.state.test1+''}</h2>
<h2>{this.state.test2+''}</h2>
<h2>{this.state.test3.toString()}</h2>
{/* 对象作为子类 -- 错*/}
{/* <h2>{this.state.friend}</h2>*/}
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
嵌入表达式
提纲:
- 运算符表达式
- 三元运算符
- 函数调用
- 对象解构
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
firstName: 'kobe',
lastName: 'bryant',
isLogin: true
}
}
render() {
// 对象的解构
const { firstName, lastName, isLogin } = this.state
return (
<div>
{/* 运算符表达式 */}
<h2>{firstName + ' ' + lastName}</h2>
<h2>{20 * 50}</h2>
{/* 三元运算符 */}
<h2>{isLogin ? '欢迎回来' : '请先登录'}</h2>
{/* 函数调用 */}
<h2>{this.getFullName()}</h2>
</div>
)
}
// 区别于setState,因为setState在类内,需要bind,getFullName不在父类中,自己定义所以不用bind
getFullName() {
return this.state.firstName + " " + this.state.lastName
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
绑定属性
纲要:
- 绑定普通属性
- 绑定class
- 绑定style
function getSizeImage(imgUrl, size) {
return imgUrl + `?param=${size}y${size}`
}
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
title: '标题',
imgUrl: 'http://p4.music.126.net/-8A5EGZ8hz3byulhycfk2Q==/109951165108319236.webp',
link: 'http://www.baidu.com',
active: true
}
}
render() {
const {title, imgUrl, link, active} = this.state
return (
<div>
{/* 绑定普通属性 */}
<h2 title={title}>我是标题</h2>
<img src={getSizeImage(imgUrl, 140)} alt="" />
<a href={link} target="_blank">百度一下</a>
{/* 绑定class */}
<div className="box">我是div元素</div>
<div className={"box " + (active ? 'active' : '')}>我是div元素</div>
<label htmlFor=""></label>
{/* 绑定style */}
<div style={{color: 'red', fontSize: '50px'}}>我是div,绑定style属性</div>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
绑定事件
纲要:
- 绑定事件不像html一样onclick,使用驼峰:onClick
- 绑定this的四种方案
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
message: '按钮发送了点击!!',
counter: 100
},
this.btnClick3 = this.btnClick3.bind(this) // 方案2:构造器绑定
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.btnClick}>按钮1</button>
{/* 方案1:通过bind绑定this */}
<button onClick={this.btnClick2.bind(this)}>按钮2</button>
{/* 方案2:构造器绑定 */}
<button onClick={this.btnClick3}>按钮3</button>
{/* 方案3:定义函数时,使用箭头函数 */}
<button onClick={this.btnClick4}>按钮4</button>
{/* 方案4(推荐):直接传入一个箭头函数,在箭头函数中直接传入需要执行的函数*/}
<button onClick={() => { this.btnClick5() }}>按钮5</button>
</div>
)
}
btnClick() {
console.log('按钮发送了点击!!');
}
btnClick2() {
console.log(this.state.message);
}
btnClick3() {
console.log(this.state.message);
}
// 箭头函数中永不绑定this,ES6中给对象增加属性的方式:class.field
btnClick4 = () => {
// 如果使用this这里不存在就会往上层找
console.log(this.state.counter);
}
btnClick5() {
console.log(this.state.counter);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
传递参数
提纲:
- 传递event
- 传递函数参数,使用箭头函数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- React开发依赖 -->
<script src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 生产环境中不建议使用 -->
<script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
movies: ['大话西游', '海王', '流浪地球', '盗梦空间']
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={ (e)=>{ this.btnClick(e) } }>按钮</button>
<ul>
{
this.state.movies.map((movie, index, arr)=> {
return <li onClick={(e) => {this.liClick(movie, index, e)}}>{movie}</li>
})
}
</ul>
</div>
)
}
btnClick(event) {
console.log(event);
}
liClick(movie, index, e) {
console.log(movie + ': ' + index);
console.log(e);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
条件渲染
Part one:
- 逻辑判断
- 三元运算符
- 逻辑与
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- React开发依赖 -->
<script src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 生产环境中不建议使用 -->
<script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
isLogin: true
}
}
render() {
{/* 对象的解构 */}
const {isLogin} = this.state
{/* 逻辑判断 */}
let welcome = null
if (isLogin == true) {
welcome = <h2>欢迎回来</h2>
} else {
welcome = <h2>请先登录!</h2>
}
return (
<div>
{/* 三元运算符 */}
{welcome}
<button onClick={()=>{this.loginClick()}}>{isLogin ? '退出' : '登录'}</button>
<hr/>
{/* JS中最优方案:逻辑与 */}
<h2>{isLogin && '你哈啊,zhiyu'}</h2>
</div>
)
}
loginClick() {
this.setState({
isLogin: !this.state.isLogin
})
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
part two:
- 利用
style={{CSS属性名:属性值}}进行动态条件判断
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- React开发依赖 -->
<script src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 生产环境中不建议使用 -->
<script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
isLogin: true
}
}
render() {
const { isLogin } = this.state
return (
<div>
<button onClick={e => this.loginClick()}>{isLogin ? '退出' : '登录'}</button>
<h2 style={{display: isLogin ? 'block' : 'none'}}>你好啊,zhiyu</h2>
</div>
)
}
loginClick() {
this.setState({
isLogin: !this.state.isLogin
})
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
列表渲染
- 列表遍历
- 列表过滤
- 列表截取
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- React开发依赖 -->
<script src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 生产环境中不建议使用 -->
<script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
names: ['javascript', 'java', 'C#', 'Cpp', 'Python'],
numbers: [100, 120, 123, 501, 201, 520, 310]
}
}
render() {
const {names, numbers} = this.state
return (
<div>
<ul>
{
names.map((item)=> {
return <li>{item}</li>
})
}
</ul>
<hr/>
<p>数字列表:过滤</p>
<ul>
{
numbers.filter(number => number >= 50)
.map(item => <li>{item}</li>)
}
</ul>
<hr/>
<p>数字列表:截取</p>
<ul>
{
numbers.slice(0, 4).map(item => <li>{item}</li>)
}
</ul>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
案例--书籍计算
综合应用以上JSX语法:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>书籍内容填充</title>
<style>
table {
border: 1px solid #000;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th, td {
border: 1px solid #000;
padding: 10px 10px;
text-align: center;
}
th {
background-color: #bdc3c7;
}
.count {
margin: 5px
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- React开发依赖 -->
<script src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 生产环境中不建议使用 -->
<script src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script src="./formatUtil.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
books: [
{
id: 1,
name: '《算法导论》',
date: '2006-9',
price: 85.00,
count: 1
},
{
id: 2,
name: '《黑豹红狼》',
date: '2021-5',
price: 57.80,
count: 1
},
{
id: 3,
name: '《乡下人》',
date: '2021-5',
price: 66.00,
count: 1
},
{
id: 4,
name: '《切尔诺贝利的午夜》',
date: '2021-3',
price: 62.40,
count: 1
},
{
id: 5,
name: '《认识世界:古代与中世纪哲学》',
date: '2021-4',
price: 71.90,
count: 1
}
]
}
}
render() {
return this.state.books.length ? this.renderBooks() : this.renderEmptyTips();
}
getTotalPrice() {
{/*let totalPrice = 0
for (let item of this.state.books) {
totalPrice += item.price * item.count
}
return formatPrice(totalPrice)*/}
const totalPrice = this.state.books.reduce((pre, item)=>{
return pre + item.price * item.count;
}, 0)
return formatPrice(totalPrice);
}
removeBook(index) {
this.setState({
books: this.state.books.filter((item, indey) => index != indey)
})
}
changeBookCount(index, count) {
let duplicateOfBooks = [...this.state.books]
console.log(duplicateOfBooks[index].count);
if (duplicateOfBooks[index].count + count >= 0) {
duplicateOfBooks[index].count += count
this.setState({
books: duplicateOfBooks
})
}
}
renderBooks() {
const {books} = this.state
return (
<div>
<table>
<thead>
<th></th>
<th>书籍名称</th>
<th>出版日期</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>购买数量</th>
<th>操作</th>
</thead>
<tbody>
{
books.map((item, index) => {
return (
<tr>
<td>{index+1}</td>
<td>{item.name}</td>
<td>{item.date}</td>
<td>{formatPrice(item.price)}</td>
<td>
<button onClick={e => this.changeBookCount(index, -1)}>-</button>
<span className='count'>{item.count}</span>
<button onClick={e => this.changeBookCount(index, +1)}>+</button>
</td>
<td><button onClick={() => this.removeBook(index)}>移除</button></td>
</tr>
)
})
}
</tbody>
</table>
<h2>总价格:{this.getTotalPrice()}</h2>
</div>
)
}
renderEmptyTips() {
return (
<h2>购物车为空~!</h2>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
React组件化开发
render函数能返回什么类型
React元素
- JSX创建
数组或fragments
Protals
字符串或数值类型
布尔类型或null
生命周期
常用的生命周期:
Constructor
- 通过给this.state复制对象来初始化内部的state
- 为事件绑定实例(this)
componentDidMount
- 依赖于DOM的操作
- (推荐)发送网络请求
- 添加订阅
componentDidUpdate
- 组件更新
- 网络请求
componentWillUnmount
- 清除操作
整个生命周期:
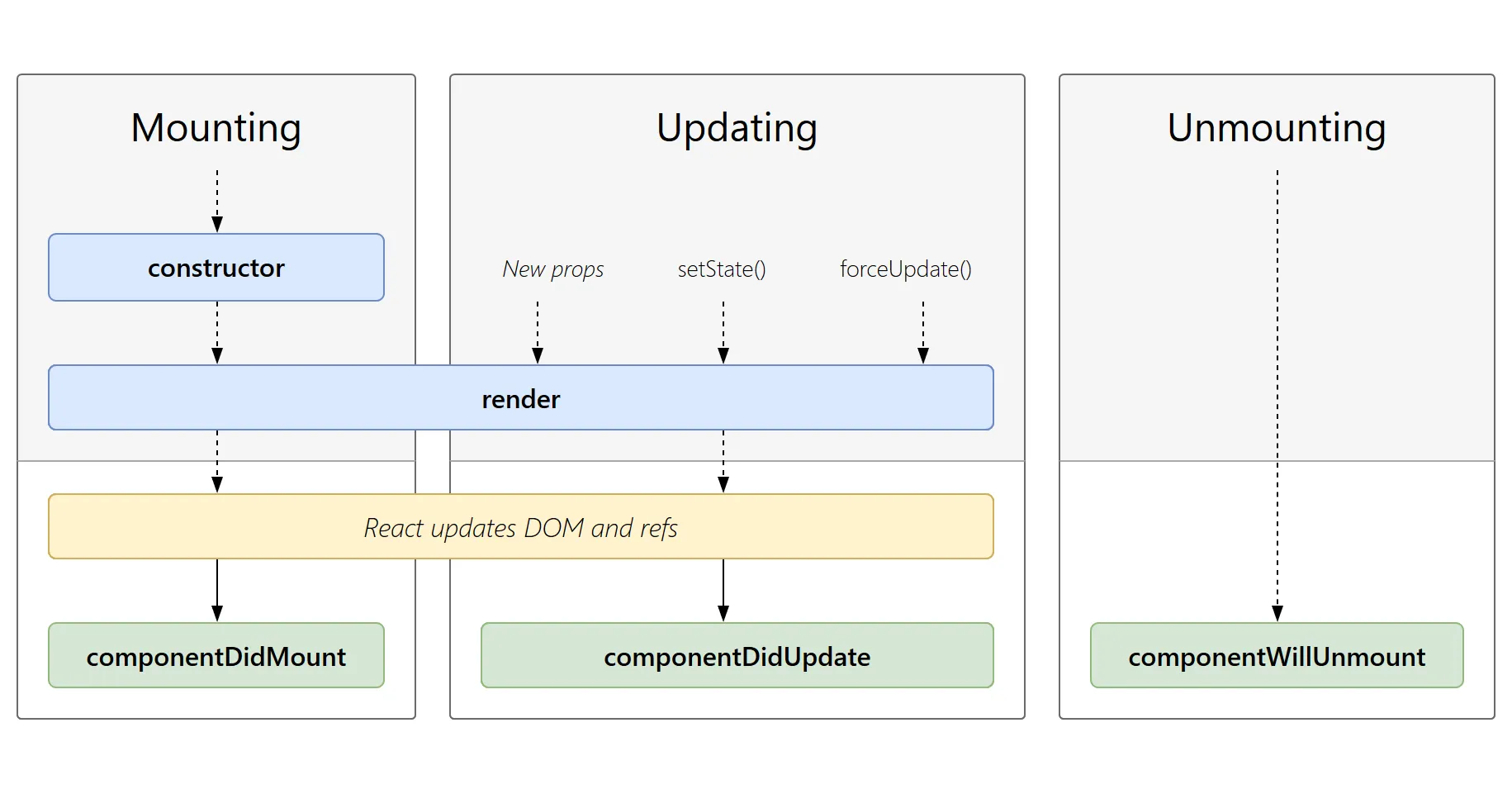
具体可以参考:https://www.runoob.com/react/react-component-life-cycle.html
or https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/state-and-lifecycle.html